Architectural Paint Research
Historic paint research is used to identify the nature of layers of paint and give an indication of age. The paint may have been applied to buildings, architectural features or historic items. Generally, small samples of paint are removed and analysed in the laboratory using a variety of techniques.
Inspiratech have analysed a wide range of paint layers for public and private industry. Projects include:- Historic buildings
- Preservation of historic features, eg medieval artifacts
- Railway stations, bridges and warehouses
- Conversion of use projects
- Wrought iron gates and railings and
- Council buildings
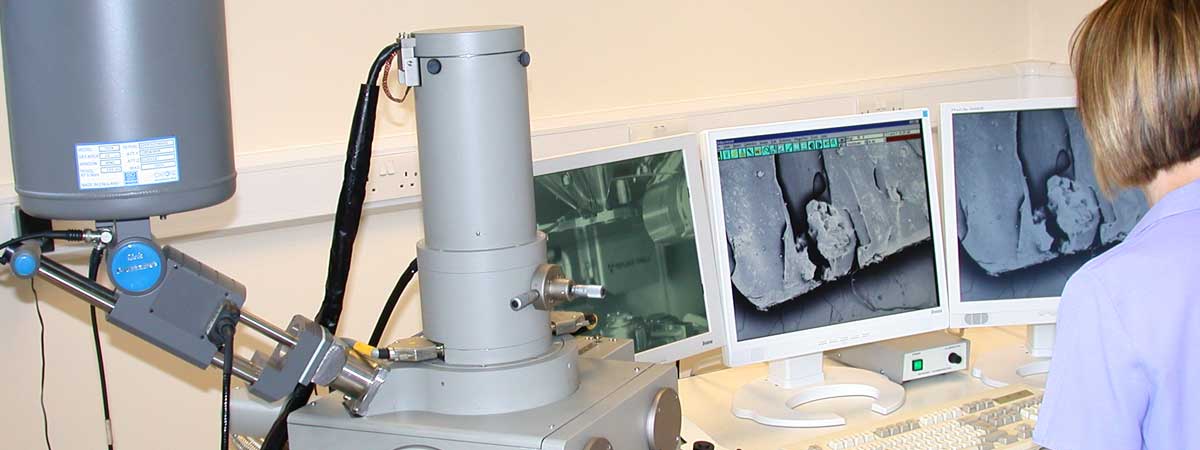
A typical analysis would involve sectioning the paint sample, mounting in resin and polishing. The cross-section is examined in the scanning electron microscope, to produce images, which reveal details of each layer. Individual particles of pigments and fillers, such as lead and other traditional pigments, limestone and titanium dioxide are identified by chemical analysis, using x-ray analysis (EDS).
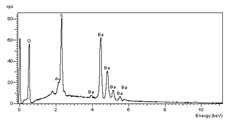
EDS spectrum for barium sulphate
Information obtained includes:- the number of paint layers
- the thickness of each layer and
- the chemical analysis and size of the fillers in each layer.
Filler analysis is used to identify any metallic layers such as gilding, provide environmental data and identify traditional pigments or treatments.
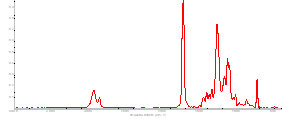
The polymer used to produce a paint or varnish may be analysed using FTIR (Fourier Transform Infra-red). The technique produces a spectrum of the layer by recording the absorption of infra-red light. The spectrum is then compared to reference spectra for polymers.