Rubber Hardness
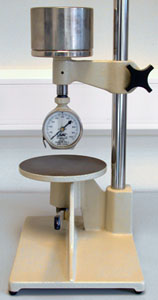
Elastomeric materials are usually measured with either a Shore A Scale Durometer or an IRHD dead load system. These tests are designed for use with samples approx 6mm thick, and a surface area sufficient to permit at least 3 test points 5mm apart, 13mm from any edge.
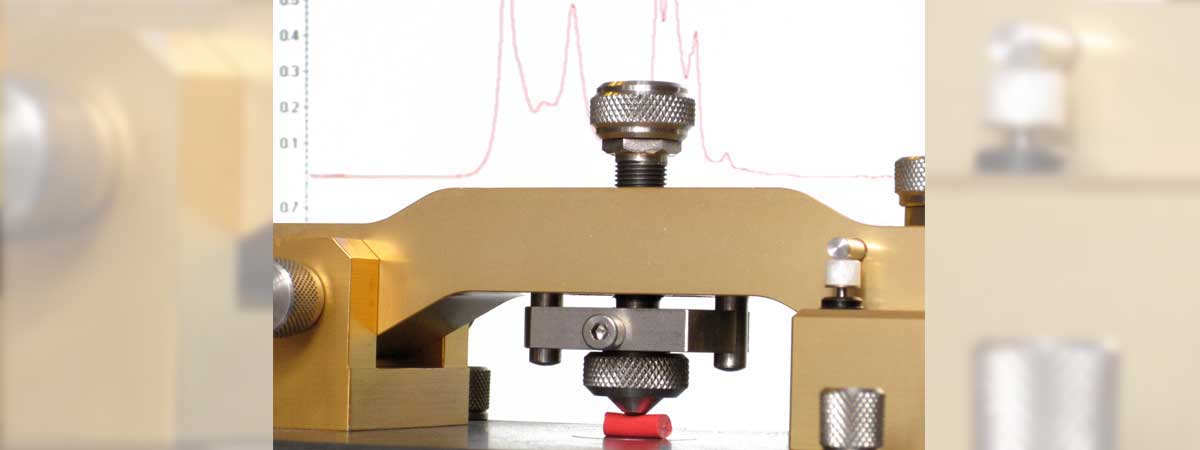
Microhardness testers, Shore "A" Micro (M), or IRHD Micro (M), are utilised to measure samples which are too small for testing with macro instruments.
Shore
The Shore type instrument is a spring loaded indentation device, in which values are obtained as a function of the viscoelastic property of the material. The truncated cone indentor, extends 0.098inch (2.5mm)) and is pressed onto the sample against an 822g spring. Each 0.001 inch of deflection of the indentor is shown as 1 degree Shore (A), therefore, the harder the material, the more the deflection, the higher the number.
Materials reading below 10 degrees and above 90 degrees can be tested using Shore O & D scales respectively. The scales "OO" is designed to read materials less than 10 Shore "O". Scales "B" & "C" are intermediate scales and the specifications are hybrids of the "A" & "D".
The microhardness tester reading Shore "A" Micro is basically a combination of "OO" Spring and "D" Indentor (set at 0.050inch (1.25mm)). The instrument is comparative and is supplied with a set of reference blocks which enable calibration to the macro "A" value.
IRHD
The IRHD (International Rubber Hardness Degrees) instrument has a spherical indentor which indents the sample under a minor and major Load. The differential indentation depth is measured and tabulated to read directly in "IRHD" degrees. The displacement/IRHD degrees conversion table is published in ISO 48 : 1994. The standard shows three different combinations of Ball & Loadings, (N) Normal, (H) High and (L) Low.
Aplications
| Material | Instrument | Examples |
| Soft rubber, sponge rubber, skinned urethane foam, cork | Shore 0 & 00 | Pad printers, fruit, tissues, automotive trim |
| Medium hard rubber, flexible polyurethane, soft polymers, felts | Shore A, Shore "A" Micro (M), IRHD, IRHD Micro (M) | General rubber parts, tyres, rollers, piano felts, sealants, seals, O-Rings |
| Medium hard rubber, polyurethane, plastics | Shore C | Automotive trim, hard rubber rollers |
| Hard rubber, rigid polyurethane, thermo plastics, epoxy resin | Shore D | Potting compounds, general plastic parts, vinyl flooring, brake pads, calendar rolls |
Standards
| ISO 48-2:2018 | Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic. Determination of hardness. Hardness between 10 IRHD and 100 IRHD |
| ISO 48-4:2018 | Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic -- Determination of hardness -- Part 4: Indentation hardness by durometer method (Shore hardness) |
| ISO 48-5:2016 | Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic. Determination of hardness. Indentation hardness by IRHD pocket meter method |
| BS EN ISO 868:2003 | Plastics and ebonite. Determination of indentation hardness by means of a a durometer (Shore hardness) |
| ASTM D1415-18 | Standard Test Method for Rubber Property-International Hardness |
| ASTM D2240-15e1 | Standard Test Method for Rubber Property-Durometer Hardness |
| (DIN 53505) | Prüfung von Kautschuk, Elastomeren und Kunststoffen; Härteprüfung nach Shore A und Shore D |
| (DIN 53519-1) | Prüfung von Elastomeren; Bestimmung der Kugeldruckhärte von Weichgummi, Internationaler Gummihärtegrad (IRHD); Härteprüfung an Normproben |
| (DIN 53519-2) | Prüfung von Elastomeren; Bestimmung der Kugeldruckhärte von Weichgummi, Internationaler Gummihärtegrad (IRHD); Härteprüfung an Proben geringer Abmessungen, Mikrohärteprüfung |